Cybersecurity for Small Businesses: Best Practices
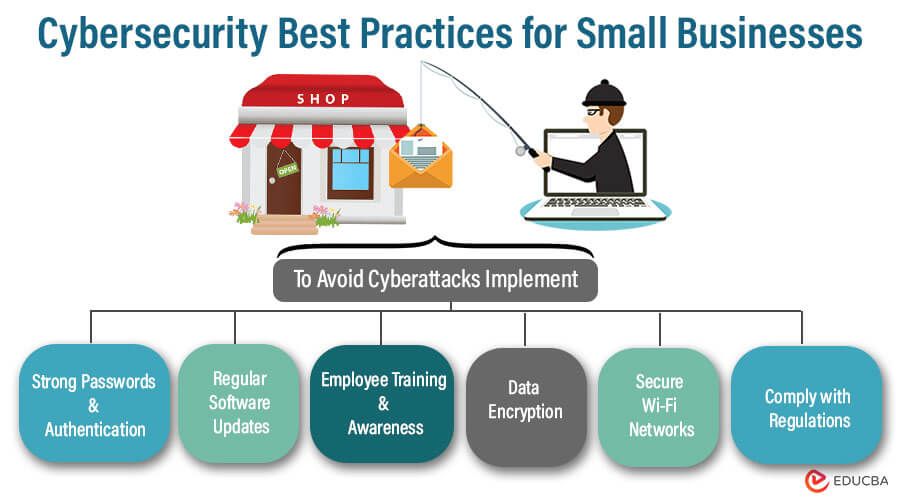
With cyber attacks on the rise, small businesses are increasingly becoming targets for hackers looking to steal sensitive data or disrupt operations. To protect your business from these threats, it’s important to implement strong cybersecurity measures. Here are some best practices to help keep your small business safe:
1. Implement a Firewall
A firewall is a critical first line of defense against cyber threats. It acts as a barrier between your internal network and external threats, monitoring and controlling incoming and outgoing traffic. Make sure to keep your firewall updated with the latest security patches to ensure maximum protection.
2. Secure Your Wi-Fi Network
Wi-Fi networks are often targeted by hackers looking to gain access to sensitive information. Secure your network with a strong password, enable encryption, and consider setting up a separate guest network for visitors. Regularly check for unauthorized devices connected to your network.
3. Train Your Employees
Human error is one of the leading causes of cybersecurity breaches. Educate your employees on best practices for handling sensitive information, identifying phishing attempts, and creating secure passwords. Conduct regular training sessions to keep cybersecurity top of mind.
4. Use Strong Passwords
Weak passwords are one of the easiest ways for hackers to gain access to your systems. Encourage employees to use complex passwords that include a mix of letters, numbers, and special characters. Consider implementing multi-factor authentication for an added layer of security.
5. Keep Software Up to Date
Outdated software is a common vulnerability that hackers exploit to gain access to systems. Regularly update all software and applications on your devices to patch security flaws and protect against cyber threats. Consider enabling automatic updates for added convenience.
6. Backup Your Data
Data loss can be catastrophic for small businesses, especially if it’s caused by a cyber attack. Be sure to regularly backup your data to a secure offsite location to protect against ransomware and other threats. Test your backups regularly to ensure they can be easily restored in the event of an incident.
7. Monitor Your Systems
Implementing a system monitoring tool can help you detect potential security threats before they escalate. Monitor network traffic, user activity, and system logs for any unusual behavior that could indicate a breach. Set up alerts to notify you of any suspicious activity in real-time.
8. Create an Incident Response Plan
Despite your best efforts, a cybersecurity incident may still occur. Having an incident response plan in place can help you react quickly and effectively to minimize the impact on your business. Outline the steps to take in the event of a breach, including how to communicate with customers and stakeholders.
Conclusion
Protecting your small business from cyber threats requires a proactive approach to cybersecurity. By implementing these best practices, you can strengthen your defenses and reduce the risk of a cyber attack. Stay vigilant, stay informed, and prioritize cybersecurity to safeguard your business and your customers.